Plant based sources of iron
If you don't like meat or prefer to follow a plant based or vegetarian diet, getting enough iron from plant based sources can be difficult to achieve. Difficult, but not impossible. With some careful planning it is possible for vegetarians to use plant based foods to achieve their iron needs.
What does iron do?
Iron plays an important role in oxygen transport and is a key component in red blood cells. If you are low in iron are you might feel lethargic, really tired and lacking in energy or might be easily exhausted with simple tasks. For athletes, low iron stores can mean you don't get the most out of training and underperform in competition.
How much iron do we need?
Iron recommendations vary between countries, according to age and gender, with women needing more until menopause sets in. In the UK, the general adult population is recommended a daily iron intake of 8.7mg for men and 14.8 mg for women. Australian iron recommendations are similar for men at 8mg per day while slightly higher for women at 18mg daily.
Bioavailability of plant based iron
Bioavailability is a measure of how much iron is absorbed and available for the body to use. Many factors in food can influence this - some positively, others negatively. Tannins found in tea can reduce the amount of iron available, while vitamin C in fruits and vegetables can increase the amount that is available.
There are two kinds of iron - haem iron and non-haem iron. Plant-based sources of iron fall under the latter category which aren't absorbed or quite as readily available as the haem sources which are animal based.
Since plant-based iron (non-haem) isn't as bioavailable, people following a vegetarian or vegan diet need about 1.8 times more iron which means around 14.4 - 15.7mg for men and 26.7 - 32mg of iron for women.
Plant based athletes may need 30-70% more iron than the average person depending on the type, intensity and amount of training they do. It’s worth having getting your iron status checked regularly to avoid iron deficiency and promote peak performance.
Plant based iron rich foods
The following tables list plant based sources of iron per 100g or 100ml as well as the amount in a typical serving size for each food.
Nutrition values can vary from country to country depending on soil, how foods are grown and produced. Some countries will fortify particular foods such as breakfast cereals which can result in higher values. If a food has been fortified with iron, it will usually say so on the nutrition panel.
Iron in Beans, lentils and legumes
Iron in Nuts & Seeds
Iron in Grains & cereals
Iron in Meat Alternatives
Iron in Vegetables
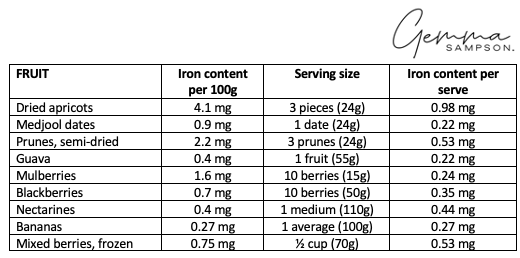
Iron in Fruit
Iron in Herbs & Spices
Iron in Milk alternatives
Iron in miscellaneous foods
As always, the most important thing to remember when eating a plant based diet is to include a wide variety of plants in every meal as each different component will add a little nutritional boost.
Gemma
Are you looking for support transitioning to a plant based diet or want to ensure you are getting the nutrients to suit your training and lifestyle? Book an online nutrition consultation to ensure you optimise your training and health.
Fuel your cycling with confidence
Do you want to know how best to fuel your training sessions? Are you keen to lose weight and optimise your performance?
The Cycling Nutrition Framework will fuel your cycling goals.